Types of Acne Explained
- jasonsdevacc
- Mar 10, 2024
- 3 min read
Acne is a common skin condition that affects individuals globally, presenting in various forms, each with its unique characteristics and treatment approaches. Understanding the different types of acne is crucial for effective management and prevention. Here, we'll delve into an exploration of acne, its causes, treatments, and preventive measures, focusing on insights from Dr. Shruti Chavan at Youthville Clinic in Andheri West, Mumbai.
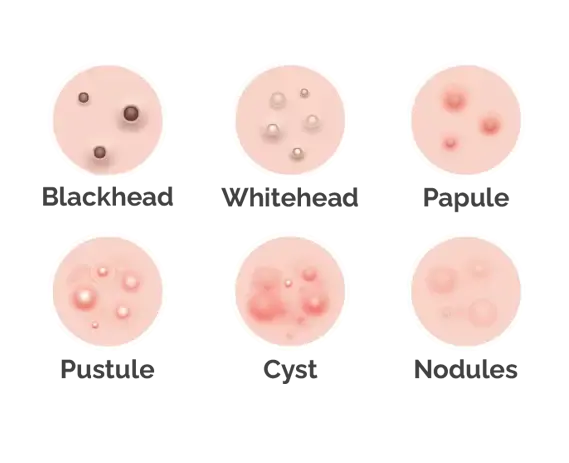
Blackheads and Whiteheads
- Blackheads (Open Comedones): These appear as small, dark spots on the skin, primarily due to clogged hair follicles. The dark color is not due to dirt but to the oxidation of sebum and dead skin cells exposed to air.
- Whiteheads (Closed Comedones): Unlike blackheads, whiteheads are formed when pores get clogged and close up, leading to small, flesh-colored bumps. They occur when oil and skin cells prevent a clogged hair follicle from opening.
Both types of comedonal acne can be influenced by factors such as hormone fluctuations, excessive oil production, and improper skincare routines.
Inflammatory Acne: Papules, Pustules, Nodules, and Cysts
- Papules and Pustules: When blackheads or whiteheads become inflamed, they can turn into papules and pustules. Papules are hard, clogged pores that are tender to the touch, while pustules are similar but filled with pus.
- Nodules and Cystic Acne: These are more severe forms of acne where the infection goes deeper into the skin, creating larger, painful lumps beneath the surface. Cystic acne, in particular, is known for its potential to scar the skin.
Factors contributing to inflammatory acne include hormonal imbalances, diet, stress, and genetics.
Causes of Acne
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations, especially during puberty, pregnancy, and menstrual cycles, can increase oil production.
- Diet and Lifestyle: High glycemic foods, dairy, and certain fats have been linked to acne, though this can vary between individuals.
- Stress: Increases in cortisol can exacerbate acne.
- Genetics: A family history of acne can increase one's predisposition.
Understanding these triggers is crucial for managing acne outbreaks effectively.
Treatments for Acne
Over-the-counter (OTC) products containing salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, and retinoids can treat mild to moderate acne by exfoliating the skin and reducing inflammation. For more severe cases, prescription medications, including oral antibiotics, contraceptive pills, and isotretinoin, might be recommended. It's important to consult a dermatologist, like Dr. Shruti Chavan at Youthville Clinic, for a tailored treatment plan.
Cosmetic Procedures
For persistent acne and scarring, cosmetic procedures can offer solutions:
- Laser Therapy: Targets bacteria and reduces oil production.
- Chemical Peels: Removes the top layer of skin, promoting cell renewal.
- Microdermabrasion: Exfoliates the skin to improve texture and tone.
These procedures should only be performed by certified professionals and may require multiple sessions for the best results.
Prevention and Lifestyle Tips
- Regular cleansing with a gentle cleanser helps remove excess oil and dirt.
- Non-comedogenic skincare products prevent pore clogging.
- A balanced diet low in high glycemic foods and dairy may reduce acne breakouts.
- Managing stress through meditation, exercise, and sufficient sleep can also positively impact skin health.
By taking proactive steps toward skincare and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of acne outbreaks. Additionally, seeking guidance from experts like Dr. Shruti Chavan at Youthville Clinic in Andheri West, Mumbai, can offer personalized advice and treatment options tailored to individual needs, ensuring a holistic approach to acne management and prevention.






Comments